
In preimplantation genetic diagnosis, because it is necessary to take cell samples from the embryo, it can only be done in cases of in vitro fertilization when multiple embryos are needed.
Additionally for in vitro fertilization, it will be done by microscopic insemination where one sperm is inserted directly to the oocyte in order to avoid the mixing of DNA of other sperm.
In order to collect multiple mature oocytes from the ovary, the follicles will be allowed to develop while utilizing hormones and injections.
As for the ovulation induction methods, there are those such as “low stimulus”, “medium stimulus”, and “high stimulus”, but the method will be chosen based on each patient’s situation.
When the oocytes have matured, the oocyte pick-up (OPU) will be done by aspiration. The collected oocytes and sperm will be fertilized by ICSI where the sperm is inserted directly into the oocyte under a microscope.
The embryos that were made by ICSI are then cultured, and after a becoming a 6-8 cell stage or blastocyst a hole will be opened in the thin translucent layer known as the zona pellucida, and from that hole cells will be extracted and then tested.
It is known that even if cells are extracted that there will be no effect on the embryo itself.
As for the extracted cells, they will be used in the test of PGD, and each embryo will be diagnosed on whether or not there are anomalies.
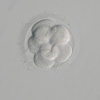
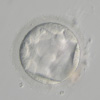
8 Cell Stage Blastocyst
According to the test, the embryo that is diagnosed as favorable will be transferred to the uterus.
As for the embryos that are not transferred, it is possible for them to undergo cryopreservation for later use, be discarded, or donated to research at the patient’s discretion.
We are providing the general information about Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis.